What Best Describes the Metabolic Effects of Catecholamines
These results were obtained by using different methods such as the adrenal medulla ablation in animals pharmacological sympathectomy adrenaline and noradrenaline infusion α- or β-blockades and marked adrenaline. Under physiologic conditions infusing catecholamine is associated with enhanced rates of aerobic glycolysis resulting.
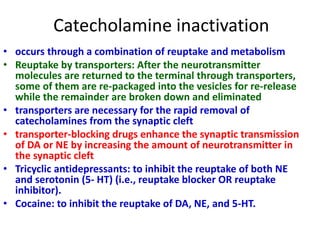
Biosynthesis Of Catecholamines
We hypothesized that OSA is associated with worse insulin resistance and lower.

. Many patients treated with clozapine go on to develop metabolic syndrome at a higher rate than the general population which predisposes them for Type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Obstructive sleep apnea OSA has been implicated in the pathophysiology of metabolic syndrome. Epinephrine increases the basal metabolic rate with consequent increase of the nonfacultative thermogenesis.
High or low levels of individual catecholamines can lead to a range of symptoms. Catecholamines reduce the amount of blood that flows to the skin and intestines but increase the amount of blood going to the brain heart and. From the reviewers point of view the definition of the term metabolic is important in determining the scope of the review.
Here I provide historical perspective describe sources and meanings of plasma levels of catecholamines and their metabolites present a model of a sympathetic noradrenergic neuron that conveys how particular aspects of sympathetic nervous function affect plasma levels of catecholamines and their metabolites and apply the model to understand. THE MANAGEMENT of acute cardiac failure following both myocardial infarction and intracardiac operations has included the use of a variety of catecholamines such as epinephrine levarterenol Levophed bitartrate and metaraminol Aramine bitartrate. Metabolism refers to the countless chemical processes going on continuously inside the body that allow life and normal functioning.
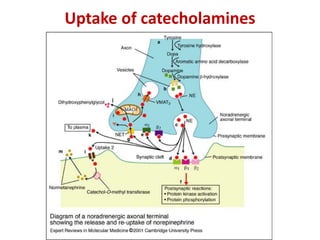
Your metabolic rate is influenced by many factors including age gender muscle-to. Steps in catecholamine metabolism were laid out several decades ago with monoamine oxidase MAO dominating intra-neuronal metabolism and catechol-O-methyltransferase COMT extra-neuronal metabolism. Adrenergic Receptors and Mechanism of Action The physiologic effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine are initiated by their binding to adrenergic receptors on the surface of target cells.
Until now catecholamines were the drugs of choice to treat hypotension during shock states. The immediate effects of catecholamines include. These are characterized by a constellation of metabolic side-effects which include dysregulation of glucose insulin plasma lipids and body fat.
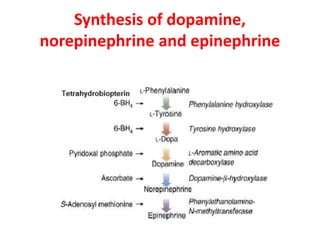
In summary intracellular catecholamines represent an accumulated product which turns synthesis off but extracellular catecholamines represent a depleted reserve and stimulate further synthesis. Catecholamines however also have marked metabolic effects particularly on glucose metabolism and the degree of this metabolic response is directly related to the beta2-adrenoceptor activity of the individual compound used. The sections below outline these in more detail.
The amount of kilojoules your body burns at any given time is affected by your metabolism. Up to 10 cash back Catecholamines have been shown to stimulate respiratory cardiac metabolic and thermoregulatory functions. They also have indirect effects mediated through changes in hormone secretion as.
The basis for their choice is the inotropic effect of these substances. Conversely the works undertaken in animals are more unanimous and suggest that physical training can increase the capacity to secrete adrenaline via an. 2 Stress to the body results in an increase in heart rate blood pressure muscle strength mental alertness blood glucose levels and breathing.
The results are more conflicting than in men and the physical training type aerobic or anaerobic effects on catecholamine response remain to be specified. Low blood glucose concentration and high blood potassium concentration are examples of __________ stimuli for an endocrine gland. These are characterized by a constellation of metabolic side-effects which include dysregulation of glucose insulin plasma lipids and body.
Its metabolic effects are anabolic favoring for example synthesis of glycogen triacylglycerols and protein. The topic of the metabolic effects of catecholamines is one of interest to pharmacologists physiologists and biochemists alike. Catecholamines however also have marked metabolic effects particularly on glucose metabolism and the.
In women studies remain scarce. Its contribution to insulin resistance is complicated by obesity and puberty. Constricting the blood vessels in the skin Increasing glucose in your bloodstream Increasing your cardiac output Making you feel excited Opening up your lungs Retaining sodium Sending more blood flow to your skeletal muscles Slowing down the.
This lipolytic effect of catecholamines is of vital importance when there is glucose deficiency and consequently ATP and energy deficiency thus catecholamines lipids are use as an alternate fuel. Insulin is composed of 51 amino acids arranged in two polypeptide chains designated A and B which are linked together by two disulfide bridges Figure 233A. Chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids that travel through the blood and regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body are called ________.
The immediate product of MAO acting on dopamine DA is the catecholaldehyde 34-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde DOPAL which is detoxified by aldehyde. You explain to him that cholesterol is important. It will be appreciated that the catecholamines have indirect effects on metabolism which are mediated through physiological changes - heart rate blood flow etc.
Abnormal dopamine levels High dopamine levels may lead to the. John tells you that cholesterol is bad and should be eliminated from the diet. This term is generally defined by biochemists as including all chemical processes.
Read the full fact sheet. This is achieved by increasing the O2. Catecholamines are produced by the adrenal glands as a reaction to stress.
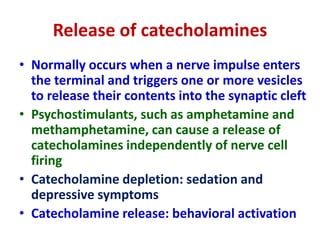
Both turn on factors hormonal humoral and neural stimuli and turn off factors feedback inhibition and others may be modulated by the activity of the nervous system. Following secretion into blood the catecholamines bind loosely to and are carried in the circulation by albumin and perhaps other serum proteins. Once secreted the catecholamines not only enter the blood but also have a feedback effect on the secretory cell elevating cAMP levels and activating tyrosine hydroxylase.
The Catecholamine Theory Of Depression

Biosynthesis Of Catecholamines

Pdf Non Hemodynamic Effects Of Catecholamines
The Catecholamine Theory Of Depression
What Is The Effect Of Thyroid Hormones On Catecholamines Quora

Figure 1 Pathogenesis Of Hyperglycemia Hyperglycemia Results From Increased Hepatic Glucose Production And Impair Metabolic Disorders Growth Hormone Hormones

Pdf Non Hemodynamic Effects Of Catecholamines

Pdf Non Hemodynamic Effects Of Catecholamines

Biosynthesis Of Catecholamines
Biosynthesis Of Catecholamines
Biosynthesis Of Catecholamines

Image Result For Neurotransmitters Inhibitory Or Excitatory Neurotransmitters Medical Facts Pharmacology Nursing

Pin By Ramona Collazo On Nursing Adrenal Cortex Pharmacology Nursing Med Surg Nursing

Pdf Non Hemodynamic Effects Of Catecholamines
Biosynthesis Of Catecholamines


Comments
Post a Comment